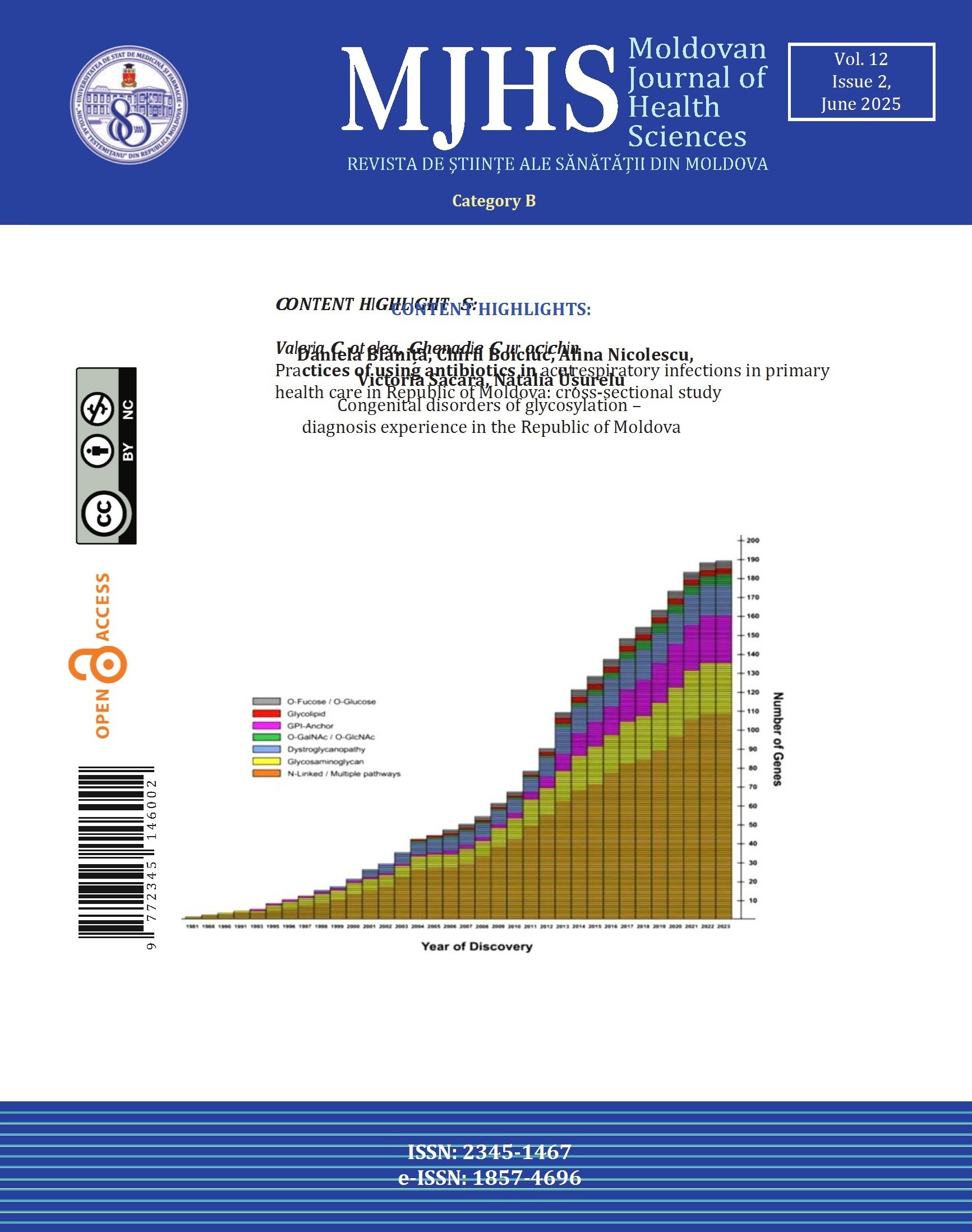
Congenital disorders of glycosylation - diagnosis experience in the Republic of Moldova
https://doi.org/10.52645/MJHS.2025.2.01
Abstract
Introduction
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) represent a group of rare diseases with multisystem involvement and exponential expansion, characterized by defects in the glycosylation process, which is essential for the proper functioning of proteins and lipids. These often manifest under the guise of other pathologies. The objective of the study was to diagnose CDG using Isoelectric Focusing of Transferrin (IEFT) in the Republic of Moldova and to identify diseases that mimic CDG.
Material and methods
Following medical-genetic consultations at the Institute of Mother and Child, 320 patients suspected for CDG were selected. History, clinical and paraclinical data were collected, and the proposed research questionnaire was completed. After signing the informed consent, the biological samples (serum, plasma, urine, DNA, DBS) were collected from all patients. Screening serum using the IEFT method was performed for 150 patients due to limited availability of reagents. For cases with negative CDG results, selective molecular-genetic tests such as MLPA, CGH-array, WES/WGS were performed.
Results
Clinical and paraclinical examination of patients suspected CDG revealed multisystem involvement in 99.1% of cases, predominantly affecting the central nervous system in 92.2%. System and organ evaluation showed that, in addition to neurological damage there were skeletal (22.5%), renal (10.9%), ophthalmological (38.8%), muscular (22.5%), hepatic (20.9%), cardiac (40.6%), auditory (5.9%), pulmonary (3.8%), and gastrointestinal (29.4%) involvement. Analysis of 150 serum samples by IEFT method identified 3 positive cases for CDG. Molecular genetic testing revealed additional two CDG cases with negative IEFT and over 50 rare pathologies that manifest under the guise of CDG.
Conclusions
Clinical heterogeneity and disruptions in various biological pathways contribute to the complexity of CDG diagnosis. The clinical overlap of genetic diseases represents a considerable challenge for clinicians, as similar symptoms between different genetic conditions can lead to confusion and delay in identifying the disease.