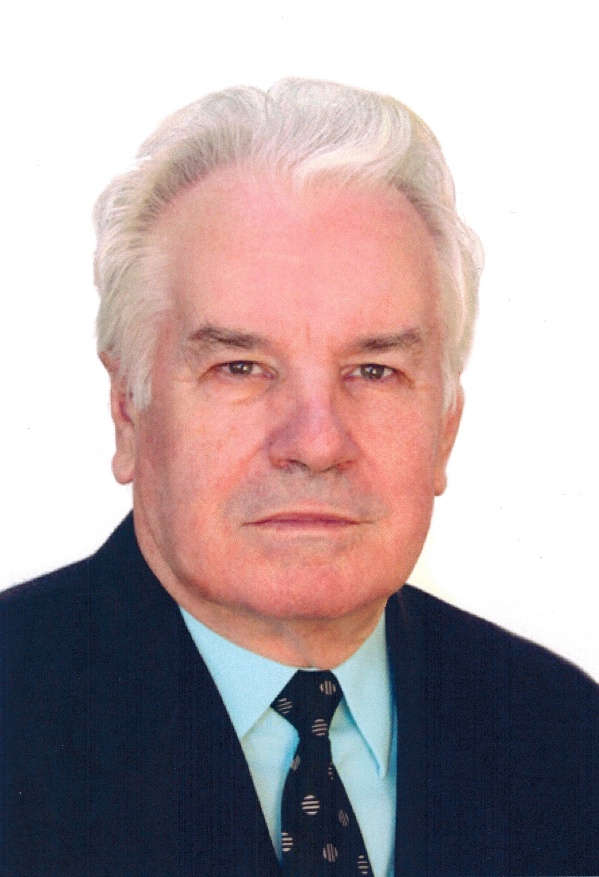
Medicine is a fascinating field that demands sacrifices. Those who are passionate about this profession devote their entire lives to studying for the benefit of human health and conducting profound research, so that later their scientific contributions may be reflected in innovation and medical practice. One such individual is Professor Nicolae Fruntașu, who turns 90 and who, alongside his teaching career, has dedicated himself to morphological research, an area in which he has distinguished himself as a renowned specialist.
Nicolae Fruntașu was born on January 13, 1935, in Cuhureștii de Sus, Soroca County, Romania, into a family of farmers for whom hard work was paramount.
In 1942, he began his primary education, and in 1949, he graduated from the local General Education School. That same year, he was admitted to the Medical College in Soroca. In 1952, Nicolae Fruntașu enrolled at the State Medical Institute in Chișinău.
After graduating in 1958, Nicolae Fruntașu was assigned to Ciutulești, Florești district, where he began working as chief physician. Medical services were provided to six villages within a radius of 15–16 km, serving a population of approximately 10,000 residents. He then worked for three years as a district physician, a period that became a true “university of life” for him.
Gaining clinical experience, Nicolae Fruntașu felt ready to embrace teaching. Thus, in 1961, he was hired as an assistant professor in the Department of Human Anatomy. His first steps in morphology were guided by Professor Boris Perlin, an experienced specialist, erudite scholar, and dedicated mentor, from whom he learned the techniques and methods of teaching the discipline.
A year later, he was offered the opportunity to research “The Innervation of the Human Knee Joint”. He pursued the topic with passion and diligence, and within a year and a few months, he presented his research project to his supervisor. In 1964, he successfully defended his doctoral dissertation in medical sciences. That same year, he was transferred to the Department of Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery as an assistant professor, and three years later, he earned the title of Associate Professor. In 1967, he was appointed head of the Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery Course at the Faculty of Continuous Medical Education. Starting in the 1970s, Professor Fruntașu shared his knowledge of human anatomy with colleagues from the department, as well as with those from clinical departments, dedicating himself to the continuous education of medical professionals for the next 41 years.
Professor Nicolae Fruntașu’s methodological and teaching activities included developing curricula and thematic plans for continuing medical education courses. Introduced in the 1990s based on the Russian school model, these courses covered various medical fields: surgery, traumatology, otorhinolaryngology, neurosurgery, urology, anesthesiology, dentistry, endoscopy, and ultrasonography.
Nicolae Fruntașu continuously improved his knowledge and professional competencies. For this purpose, collaborations were established with the Department of Clinical Anatomy at the Central Institute for Medical Advancement in Moscow, allowing faculty and scientific staff to attend continuous medical education development courses, including international ones, every two years.
Upon being transferred to another faculty and at the suggestion of Academician Vasile Anestiadi, Nicolae Fruntașu decided to change the focus of his research for his habilitation thesis to “The Biomorphosis of the Human Aorta”. He employed complex study methods to investigate histochemical and morphometric manifestations in the aortic wall components under the influence of aging factors. In 1994, he was awarded the title of Doctor Habilitated in Medical Sciences, and in June of that year, he received the academic rank of Professor. From 2008 to 2020, he served as a consulting professor.
Professor Nicolae Fruntașu’s scientific activity has resulted in 230 publications, including three monographs, numerous methodological works, five inventions, and 76 innovations. He has supervised three doctoral students and guided the development of several master's theses. He actively participated in numerous congresses, conferences, and symposia, presenting scientific papers and theses.
Beyond his professional responsibilities, Nicolae Fruntașu played an active role in the social life of his institution and country. He led a team of students in establishing a recreational camp in Sergheevka, Ukraine. For seven consecutive years, he was a member of the admissions committee of the State Medical Institute in Chișinău; for five years, he served as the president of the Union Office of the Faculty of General Medicine; for ten years, he was vice-president of the Specialized Scientific Council for Doctor Habilitated Thesis Defense (DH 14.92.06 – theoretical profile); and he participated in organizing central and local government elections 11 times, including nine times as chairman of the electoral commission.
For several decades, Nicolae Fruntașu actively participated in intra- and inter-university sports competitions as a member of faculty teams in basketball, volleyball, and checkers.
Professionally, he stood out for his responsibility, integrity, passion, and dedication, devoting 59 years of his life to Alma Mater and the education of medical specialists. Reflecting on his multifaceted career, he considers his dreams fulfilled, as he accomplished everything he set out to do in teaching, research, and social engagement.
For his outstanding contributions to the development of higher medical education, his substantial role in training highly qualified specialists, and his remarkable methodological, teaching, and scientific activities, in 2020, Professor Nicolae Fruntașu was awarded the honorary title of “Emeritus Person”.
On this momentous occasion, on behalf of the entire university community, we express our profound respect and appreciation for Professor Nicolae Fruntașu. We wish him good health, peace, and tranquility, prosperity, and many more joyful moments with his loved ones.
Happy birthday!
Emil Ceban, rector of the Nicolae Testemițanu USMF
Dr. hab. med. sciences, university professor,
corresponding member of the ASM